Understanding Rapid eLearning Prototyping
Rapid eLearning Prototyping is an integral part of the eLearning development process that focuses on creating a functional model of an eLearning course before its full design and development. This approach allows for quick and iterative evaluation and refinement of the course design based on real user feedback, leading to a more effective and engaging eLearning experience.
Prototyping in eLearning is much like prototyping in other fields such as software development or product design. It’s about creating a preliminary version of the eLearning course to check its functionality, usability, and overall design. Instead of having full-fledged courses, prototypes are often made of basic elements like textual content, images, and simple interactive exercises that mimic the proposed features and functionality of the final product. This prototype serves as a visual model, offering a sense of the course structure, content flow, navigational paths, and user interactions.
This process typically involves stakeholders, instructional designers, subject matter experts, and sometimes even a select group of learners. The prototype is shared with them for feedback and is improved iteratively based on their input until it meets the desired learning outcomes and user expectations.
One key characteristic of Rapid eLearning Prototyping is its speed. The main idea is not to produce a perfect model from the beginning, but to provide a simplistic representation of the final product that can be developed, tested, and refined in quick succession. This accelerates the development timeline, allowing instructional designers and developers to focus on creating an effective course rather than spending excessive time in revising multiple drafts.
Rapid eLearning Prototyping helps in identifying potential design and functionality issues early on in the development stage, providing valuable insights for improvement. It promotes active stakeholder and learner engagement, facilitating better understanding of the educational content and learner needs. Furthermore, it reduces the risk of project failure, as potential problems can be addressed earlier, saving time, effort, and resources in the long run.
In the next chapter, we will delve into the importance of Rapid eLearning Prototyping in creating a successful and effective eLearning course.

The Importance of Rapid eLearning Prototyping
Rapid eLearning prototyping plays an essential role in the design and development process of online courses. PulseLearning, an award-winning global learning provider, describes it as the “mock-ups of eLearning courses which are created to test and review the course design approach.” This stage of course creation is vital for several reasons.
Firstly, rapid eLearning prototyping aids in avoiding potential issues that would otherwise only become visible at the course launch. By creating mock-ups and models of the eLearning program, instructional designers, course developers, and stakeholders can identify and resolve problems before they affect the learner’s experience. Therefore, it streamlines the course development process, reducing development time and costs.
Secondly, this prototyping method allows instructional designers and developers to test multiple variables for the course design. They can experiment with different components such as page layouts, interactive elements, and the integration of multimedia before finalizing the design. This approach ensures a high-quality, efficient, optimally designed course aligned with the learning objectives.
Thirdly, prototyping offers valuable insights into how the course will be perceived by the learners, making sure the course meets their expectations and meets the defined learning objectives. This helps to ensure that the content is engaging, usable, and motivates learners to complete the training – all critical factors for an effective eLearning course.
On the administrative side, rapid eLearning prototyping is efficient and cost-effective. It allows course developers to make changes and corrections in the design phase rather than after the course launch. This capability saves time and resources, making it a budget-friendly solution, especially for extensive eLearning projects.
Through rapid prototyping, stakeholders can also become involved in the early stages of course development. This involvement helps ensure that the course aligns with the organisation’s objectives and stakeholders’ expectations, increasing the likelihood of project success.
In conclusion, rapid eLearning prototyping is an integral part of the course development process. Its benefits extend beyond time and cost savings, contributing to the creation of engaging, efficient, and effective eLearning courses by identifying and rectifying potential issues early in the design process. By ignoring the rapid prototyping stage, course developers risk producing an underperforming course and possibly having to spend additional resources on Redevelopment.

Benefits of Rapid eLearning Prototyping
Rapid eLearning prototyping brings several remarkable benefits to the educational system, professional training landscape, and to any industries seeking to implement an online learning program effectively.
Firstly, rapid eLearning prototyping reduces overall development time. Compared to traditional eLearning models, the ability to quickly create a functioning model of a course allows for faster modifications and adjustments based on feedback from stakeholders and learners. More importantly, a quick turn-around time guarantees a shorter time to market, ensuring learners can access the material promptly.
Quick decision-making is another benefit associated with rapid eLearning prototyping. Having a practical model on hand can hasten the decision-making process, particularly during the design stage. Developers can make immediate choices based on a tangible model rather than abstract concepts, thus cutting time spent on deliberation, and avoiding communication errors or misunderstandings that could lead to larger issues down the line.
Another undeniable benefit of rapid eLearning prototyping is increased cost-effectiveness. Traditionally, development resources are expended throughout the course creation process, often before any potential issues have been identified. However, by first creating a prototype, potential problems can be identified early on in development and rectified immediately, thus reducing expenditure on extensive revisions at a later stage.
Continuous enhancement of the learning product is feasible with rapid eLearning prototyping. This method offers the flexibility to not only update content anytime but also to adapt to evolving technological trends, tailoring the platform to best suit the preferences of users.
Rapid eLearning prototypes reduce the risk of failure. Stringent evaluations performed during this initial phase allows developers to assess the viability of their product. It provides insights into usability and functionality, allowing for patching any loopholes, thus increasing the chances of success.
Lastly, rapid eLearning prototyping can enhance the quality of the final product. Through iterative testing of the prototype, developers can refine the course, ensuring that learners engage with an optimal version of the platform. The fast and constant feedback allows for an efficient feedback loop to make swift improvements that meet the users’ needs.
In conclusion, rapid eLearning prototyping offers an array of benefits, ranging from time and cost efficiency to risk reduction and enhanced product quality. Recognizing these advantages can enable educators and businesses to forge more effective eLearning solutions, ultimately serving learners in the most beneficial ways possible.

Steps in Rapid eLearning Prototyping
Rapid eLearning Prototyping is a sophisticated process that enables the creation of highly effective eLearning courses. The process involves several steps, each crucial to the development of a successful prototype.
Step 1: Identify Scope and Objectives
The first step in rapid eLearning prototyping is defining its scope and objectives. You need to identify what you want the eLearning course to achieve. This involves understanding the skills or knowledge you want the learners to acquire and defining the learning goals.
Step 2: Content Gathering and Analysis
After determining the scope and objectives, the next step is to gather and analyze content. You need to collect relevant information that will make up your online course. This step involves thoroughly researching your subject matter, collecting data from different sources, then analyzing this data for relevance.
Step 3: Storyboarding
Storyboarding is an integral step in most digital design processes, including rapid eLearning prototyping. The storyboard presents a graphical illustration of how the eLearning course will flow. It includes sketches of each screen page, showing the learning content, visual elements, interactions, etc.
Step 4: Designing the User Interface
The next step is designing the user interface. The UI should be user-friendly and intuitive, enabling learners to interact with the online course without hassle. The user interface should also reflect the learning objectives of your eLearning course.
Step 5: Prototype Development
After designing the UI, you begin the phase of prototype development. This step involves creating a simplified model of your eLearning course. The prototype may not include all the features and functionalities of the final course but should give stakeholders a clear preview of the eLearning course.
Step 6: User Testing
User testing is an evaluation of the prototype by the intended eLearning course users (the learners). This stage is necessary to validate the prototype’s usefulness and effectiveness. The participants in the testing phase can provide practical feedback, which could lead to iterations and improvements in the prototype.
Step 7: Refinement and Development
Based on user feedback, the prototype is then refined and developed further until it meets the desired learning outcomes. This process can be repeated several times, with each iteration improving upon the last. When the prototype passes user testing and fulfills the objectives, you can then proceed to the next step.
Step 8: Finalizing the eLearning Course
This is the last step in rapid eLearning prototyping. You finalize the course, integrating all the feedback from testing, and make it ready for launch. This also includes Quality Assurance (QA) checks to ensure that the course functions properly.
Rapid eLearning prototyping can be quite dynamic, with steps overlapping or being revisited based on feedback and changes in needs. However, iteratively moving through these steps ensures a robust, effective eLearning course is constructed in less time, fulfilling its intended purpose to the advantage of the learners.
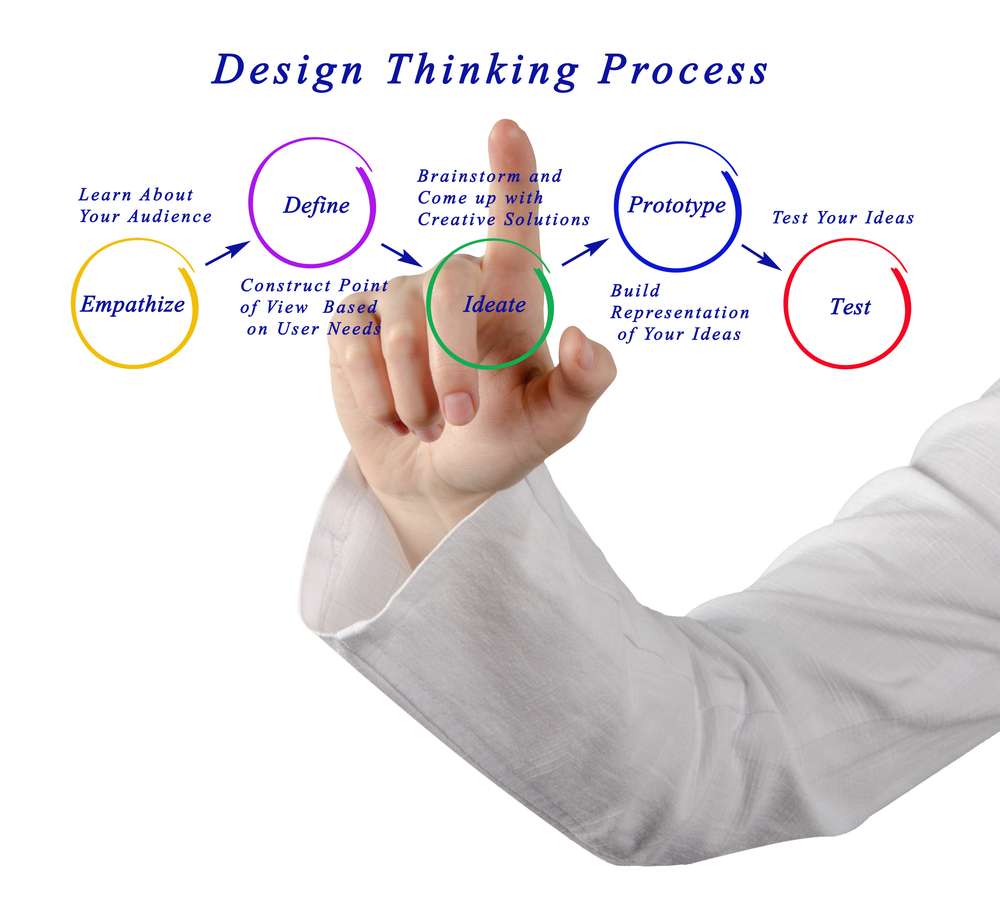
The Impact of Rapid Prototyping on eLearning Industry
Rapid prototyping stands as a game-changer in the eLearning industry. Its impact has rippled across multiple facets, successfully shifting traditional learning methods towards more adaptable, interactive, and engaging learning experiences.
First and foremost, rapid prototyping has catalysed the development pace of eLearning courses, enabling educators to churn out quality content within narrower timelines. It allows for the swift transformation of ideas into an initial model, leading to quicker identification of potential improvements or adjustments. This ability to make rapid alterations without affecting the final output’s quality ensures efficiency, saving both time and resources.
Secondly, it fosters effective collaboration among stakeholders, including educators, learners, and instructional designers. Through prototypes, all parties get a sneak peek of the educational product, enabling valuable feedback which further enhances quality. Feedback loops and iterative refinement based on real use are far easier to manage, enabling a more student-centered design approach to be adopted.
The eLearning industry also owes much of its technological advancement to rapid prototyping. It has allowed exploration into newer technologies, like AR, VR, and AI, as quick creation and testing of prototypes powered by these technologies are made possible. These technologies are seen as the bedrock of 21st-century learning, making education more immersive, dynamic and interactive.
Moreover, rapid prototyping makes eLearning more accessible. With low-cost prototypes, educational technology becomes more attainable for small-sized institutions and independent learners. This democratizing effect ensures that access to learning materials does not remain limited to those with substantial financial resources.
Rapid prototyping’s impact on eLearning’s customization is notable. As it enables modifications during development, the one-size-fits-all model is being replaced with more personalised learning experiences. Moreover, these custom-designed courses cater to a learner’s unique needs, thereby making learning more effective.
Finally, the impact of rapid prototyping has enabled eLearning to be data-driven. Insights from learners’ interaction with prototypes offer meaningful data to make informed decisions about the final design. The possibility of tracking learners’ responses and actions leads to improved designs and results in highly effective eLearning modules.
To sum it up, rapid prototyping is dramatically transforming the eLearning industry. From fostering efficiency and collaboration to driving technological advancement and customization, it is paving the way for a more learner-centric, accessible, and effective digital learning landscape. As we forge ahead in this digital age, the significance of rapid prototyping in eLearning will continue to grow, undoubtedly shaping the future of education in profound and exciting ways.

Challenges in Rapid eLearning Prototyping
While rapid eLearning prototyping yields numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. Both course creators and students can experience complications or obstacles that, if not navigated correctly, can make the process more burdensome than beneficial.
One key challenge is ensuring effective communication between teams. Developing eLearning content involves multiple parties, from subject matter experts to instructional designers, graphic designers, and developers. Each has specific tasks and responsibilities, and if communication lapses, it can cause misunderstandings, reworks, and delays. A single design change can affect several parts of the project, so each party must be clear about what is needed from them and how their role interacts with others.
Also, there is a need for an efficient feedback loop. Rapid eLearning development often involves producing multiple prototypes in quick succession. Without streamlined systems for providing feedback on each version, the development process can stall. Factors like how and when feedback is given and who provides it can greatly impact the project’s timeline and outcomes.
Content quality can be another issue in rapid eLearning prototyping. In the race to create and deploy educational content quickly, some organizations may overlook the importance of quality, leading to courses that lack depth or fail to engage students effectively. While speed is a notable advantage of rapid prototyping, it should never undermine the quality of learning.
Time pressures can also pose significant challenges. On one hand, the phrase ‘rapid prototyping’ gives the impression of a speedy process. On the other hand, the need to refine prototypes based on trials and feedback can take longer than anticipated. Managing this delicate balance is essential, though not always easy. Deadlines, stakeholder expectations and resource availability all play a factor in this tricky balancing act.
Last but not least, technological hurdles cannot be discounted. The use of software tools for course designing, development, testing, and deployment is integral to the rapid eLearning prototyping process. However, not all team members may be proficient in using these tools effectively. In some cases, the software may also lack necessary features or be prone to glitches, hence causing delays or quality issues in the final output.
Despite these challenges, rapid eLearning prototyping continues to offer innovative solutions for the development of eLearning programs. By recognizing and confronting these hurdles directly, organizations can leverage the full potential of rapid prototyping for creating effective and engaging eLearning courses.
Case Studies of Successful Rapid eLearning Prototyping
In the constantly evolving field of eLearning, there have been numerous success stories resulting from the implementation of rapid prototyping. These case studies showcase the effectiveness and impact of this concept in real-world applications.
One remarkable example is that of an online language learning platform, Wikitongues. They utilized rapid eLearning prototyping to develop an efficient and user-friendly interface. By creating several iterations of their design, the developers were able to quickly integrate user feedback and iterate upon the existing model. In the span of a few months, Wikitongues improved their user experience significantly, leading to an increase in active users and helping language learners worldwide.
In another instance, an edtech firm, LearnDash, used rapid prototyping to enhance the functionality of its Learning Management System (LMS). Initially, they encountered issues concerning unengaging learning materials and a lack of interactivity. By adopting rapid eLearning prototyping, they iteratively tested new features and obtained user feedback, which informed subsequent designs. This continuous testing and tweaking led to the development of a more effective LMS, thereby boosting student engagement and learning outcomes.
Rapid eLearning prototyping is not limited to major corporations or edtech firms. In fact, Hastac, a network of learners, teachers, and scientists, built an open-source eLearning solution using this model. The goal was to foster greater inclusivity in education. In this project, rapid eLearning prototyping facilitated the creation of a flexible learning platform, accommodating diverse learning styles and abilities. This led to a revolutionary pedagogical tool that transformed the way teaching was delivered in several communities.
Lastly, the successful application of rapid eLearning prototyping was seen in the design of an eLearning course by Harvard Medical School. The curriculum team adopted this strategy to design a course on Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics. Through prototyping, they managed to build a course with complex calculations and analysis in a format that was easily digestible. The resultant course saw high engagement and completion rates.
Through these case studies, we thus see that rapid eLearning prototyping is a powerful tool that can ultimately lead to better course structures, improved learner engagement, and measurable results. However, success in this approach requires regular iteration and constant feedback from users. Prototyping is not a one-time activity, but rather an ongoing process at the heart of effective eLearning design.
Future Trends in Rapid eLearning Prototyping
As we move forward in the world of eLearning, the emerging technology and pedagogical advances are drastically reshaping the landscape of rapid eLearning prototyping. This exciting space continues to evolve, impacting how content is created, consumed, and evaluated. Here are some potential future trends we can expect to see in rapid eLearning prototyping.
1. Personalized Learning Experiences: One of the most exciting trends is the rise of personalized learning. With advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and adaptive learning technologies, the potential for eLearning materials to be tailored to each learner’s individual needs will shape the future of learning. Rapid eLearning prototypes will be designed to accommodate these technologies, taking into account individual learning curves, preferred learning styles, and specific learning milestones.
2. Mobile Learning: The exponential growth of smartphones and tablets has made eLearning increasingly mobile. As a result, prototypes are being designed with mobile compatibility in mind, ensuring that learning materials can be accessed and consumed effectively on smaller screens. This trend will continue to rise as mobile devices become universal tools for learning and communication.
3. Microlearning: Bite-sized learning or microlearning are short, focused pieces of content designed for quick consumption. Viewing habits reveal that people prefer to consume information in small, manageable chunks. Prototyping will include considerations for creating and weaving together these smaller learning units in an effective and engaging manner.
4. Integration of VR & AR: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are progressively being integrated into eLearning materials. Future eLearning prototypes will need to accommodate these immersive learning experiences, providing a more interactive, engaging way to learn and practice skills.
5. Big Data and Learning Analytics: With the rise of Big Data, we have the ability to gather and analyze information about learning patterns, preferences, and outcomes. Prototyping tools will need to evolve to allow for tracking, gathering, and extracting insights from this data, shaping future eLearning materials.
6. Gamification: Incorporating game elements into learning is proving to be highly effective for engagement and retention. Future rapid eLearning prototyping will likely involve creating innovative ways to integrate gamification elements, making the learning experience more engaging and rewarding.
7. Social Learning: With an increasing focus on community and collaboration in learning activities, there will be a growing need to design eLearning prototypes that foster social learning. This could involve peer-to-peer interactions, shared learning spaces, and collaborative problem-solving tasks.
8. Seamless Integration with LMS: Rapid eLearning prototypes will require seamless integration with various Learning Management Systems (LMS) used by organizations. This will ensure that eLearning content can easily be updated, managed, tracked, and monitored, making it easier for educators and organizations to run their eLearning programs.
As we progress into the future, the constant evolution of rapid eLearning prototyping continues to inspire and challenge designers. The goal remains to create highly engaging and effective learning experiences that meet the growing demands of learners and educators alike. This dynamic and innovative field promises a future of learning that is more personalized, engaging, and accessible than ever before.


